Landslides
Definitions of the landslides
A ground movement (or land movement) is a more or less sudden movement of soil or subsoil down a slope.
How ground movement occur
Predisposing factors
- Terrain and slope: A rock falls from the top to the bottom due to its weight and the force of gravity acting on it. The steeper the slope, the more movement!
- The type of ground: Depending on the nature of the soil (rock, earth, or sand), erosion can be more or less significant. Instability and movement depend on the type of soil.
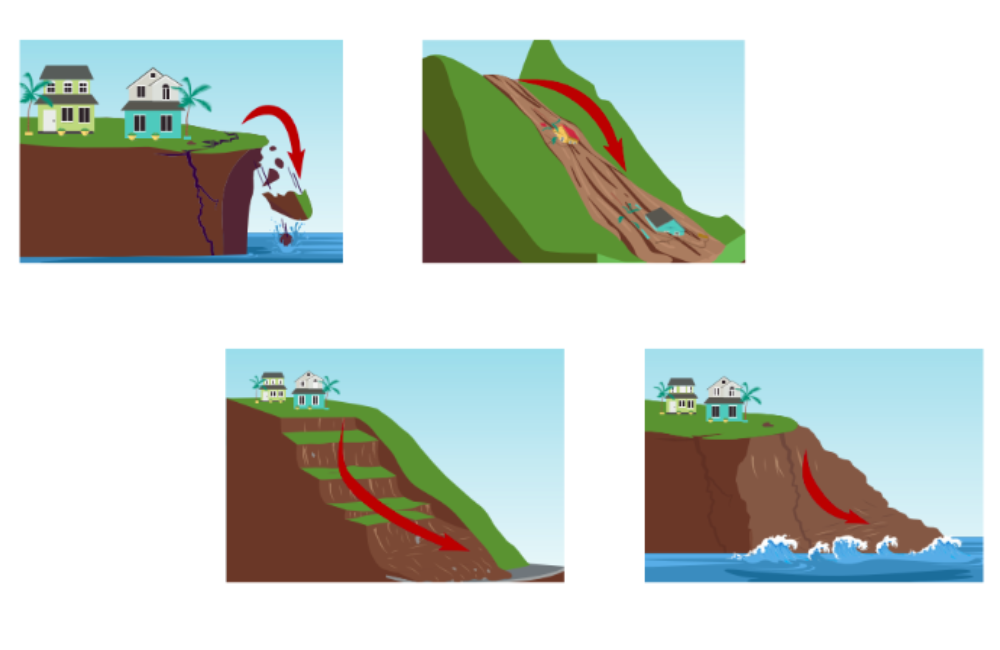
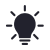







Explanatory diagram of the landslides
Factors precipitating or aggravating
- Weather conditions such as heavy rainfall, strong winds, and drought can contribute to erosion and destabilize slopes. Water can seep into cracks, weaken the materials, and reduce soil stability.
- Human activities can also aggravate soil erosion. For example, large-scale or poorly planned construction work that modifies the terrain (such as excavation or the removal of rocks) can increase instability. In addition, deforestation accelerates the process, as tree roots help stabilize the soil. However, vegetation can sometimes also contribute to rockfalls, as roots may widen cracks in already unstable blocks.
Source : Booklet teacher-cycle 4 – Project "Pare pa Pare" – French Red Cross – 2024
For more information :
Ground movement – NEMO – Government of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. Explanations to understand what land movements are, how to deal with them and protect oneself before, during, and after. (English)
Movement of ground – Geohazards – French Government. Guide, explanations, practice sheets and French schemes earthquake (French)

Menu
Home
Natural hazards
How to Protect
Risks on my island
Tool box
About
Quick access
Resources
Glossary
Contact
FAQ
Cookie policy (EU)
Pirac
OECS
CDEMA
