Climate change
What is climate change ?
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) defines climate change as: "a change in climate that is attributed directly or indirectly to human activity, alters the composition of the global atmosphere, and is in addition to natural climate variability observed over comparable time periods."
Since the end of the 18th century and the beginning of industrial activities, the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere has begun to change. The concentration of certain greenhouse gases, which had remained relatively stable for hundreds of years, has increased significantly.
The natural greenhouse effect is essential to maintaining temperatures suitable for life on Earth. However, it is now being intensified by additional greenhouse gas emissions caused by human activities. This artificial amplification of a natural process
disrupts the climate balance and leads to global warming, the impacts of which are now visible across the planet, including in the Caribbean.
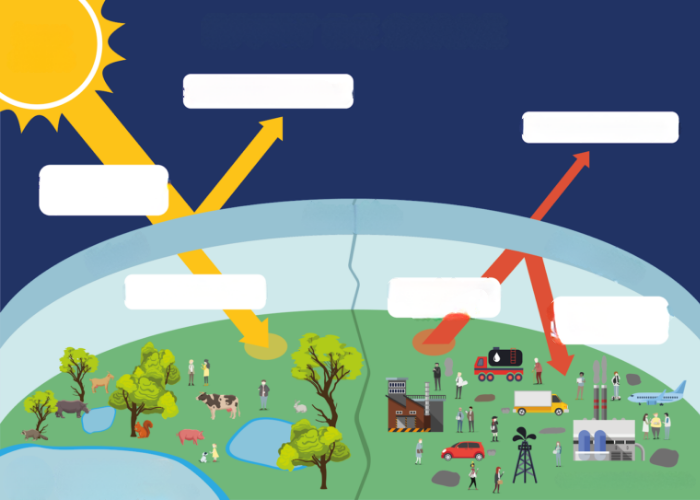











Explanatory diagram of the greenhouse effect
What is drought ?
Drought is an episode of water shortage that is long and significant enough to have an impact on the surrounding environment, that is, the soil, fauna, flora, and societies.
Lack of rainfall, known as meteorological drought
- Lack of rain, then we speak of meteorological drought
- Insufficient soil moisture, referred to as agricultural drought
- Unusually low water levels in lakes, rivers, and streams, known as hydrological drought
Source: Resource Center for Adaptation to Climate Change, Drought: What to Expect and How to Adapt
how to adapt
What are heat waves?
According to the IFRC,heat waves can be defined by " a prolonged period of abnormally high temperatures and often high humidity. They are expected to become more frequent and more severe in the future due to climate change."
Source : IFRC , Disasters, Climate Crises
The manifestations of climate change :
Climate change affects all geographical areas of the planet, with diverse manifestations:
Temperature anomalies: The Caribbean Regional Climate Centre has reported that the islands of the Caribbean have shown above-average temperatures, with readings ranging from +0.25 °C to +1.50 °C, depending on the specific location. In the region, the year 2024 will exceed the 2023 temperature, marking the warmest year recorded to date.
The ongoing drought has become a significant global concern, with its impact intensifying in the Caribbean islands. Territories such as Martinique, for example, are currently under drought surveillance due to their persistently low rainfall rates. The pomegranate is facing significant challenges, including periods of drought, heat waves, and fires that threaten ecosystems, agriculture, and daily life. The episode is significant because it marks the federation of St. Kitts and Nevis in 2015 with a drought and an increased rate of rainfall, the lowest since 1901.
Thirst in paradise: water crises are a growing problem in the Caribbean islands – International Science Council – the following is an article on the water crisis in the Caribbean.
Drought 2025: Martinique is placed on drought alert – State Actions – Article on drought episodes in Martinique.
Hot and dry: Grenada, a Caribbean island, is facing drought, heat waves, and fires. | IFRC fires | IFRC – Article on drought and heat waves in Grenada.en – esp)
As drought sets in, farmers in Saint Kitts and Nevis turn to technology for help – Article on the drought episode in Saint Kitts and Nevis in 2015 (en)
Globally, sea level rose by 20 centimeters between 1901 and 2018. The rate of rise has accelerated over the period 2006-2018 due to the thermal expansion of the oceans, the melting of the glaciers, and the withdrawal of the ice caps near the poles.
In Guadeloupe, coastal erosion linked to sea level rise (for example in Saint-François or Deshaies) has already strongly impacted the coastline. According to the BRGM, the coastline of the most exposed areas would have receded on average by 50 cm per year since the 1960s.
Oceans : The upper layers (0-700 m) of the oceans have warmed up since the 1970s, and they are currently undergoing a process of acidification.
There has also been a rapid scale-up of some cyclones that reach higher categories in a very short time.
We also observe a rapid intensification of certain cyclones that reach high categories in a very short time, strengthening their destructive nature. The passage of Hurricane Beryl in 2024 is a striking illustration: becoming the most powerful hurricane ever observed in Grenada and its dependencies, it devastated a large part of the Caribbean.
Documentation and redirect link :
According to global climate forecasts, temperatures should remain at record or near-record levels over the next five years | World Meteorological Organization
record in the next five years | World Meteorological Organization
Latin America and the Caribbean are affected by extreme weather conditions and the effects of climate (report
2024)
El Niño and climate change were manhandled Latin America and the Caribbean (report 2023)

Menu
Home
Natural hazards
Protect
Risks on each island
The toolbox
About
Quick access
Resources
Glossary
Contact
FAQ
Cookie policy (EU)
Pirac
OECS
CDEMA
